FoAR是由高等教育出版社和东南大学建筑学院联合主办的全英文学术期刊
建筑学 / 城乡规划 / 风景园林
本刊已被 A&HCI / CSCD / Scopus / DOAJ / CSTPCD 收录

01
论 文 题 目
Manuscript Title
Interscalable material microstructure organization in performance-based computational design
基于性能的运算化设计中跨尺度材料的微观结构组织
02
作 者
Authors
Sevil Yazici
Department of Architecture, Istanbul Technical University, Istanbul 34367, Turkey
03
论 文 摘 要
Abstract
Various parameters can be integrated in material-based computational design in architecture. Materials are the main driver of these processes and evaluated with the constraints related to the form, performance, and fabrication techniques. However, current methodologies mostly involve investigating already existing materials. Studies on computational material design, in which new materials are developed by designing their microstructures in response to the performative issues, are generally undertaken at the material scale, and not adopted to the architectural design process yet. To resolve this issue, the methodology titled Interscalable Material Microstructure Organization in Performance-based Computational Design (I2MO_PCD) is developed and presented in three stages, including (1) identification of different types of material microstructures, (2) computational material design, and (3) prototyping. Data-based material modelling and visualization, and algorithmic modelling techniques are utilized, followed by various performance simulations as a part of an iterative process. New microstructure organizations are designed computationally, organized under three main groups as linear-curvilinear, crystal and metaball-voronoi. The outcomes of different performance analyses, including structure, radiation, direct sun hours, acoustics and thermal bridge were compared. Thus, the role of geometrical organization of microstructures, scales and material types in different performance computations were identified, by designing and fabricating synthetic materials.
在建筑领域基于材料的运算化设计中,可以整合各种参数。材料是这些过程的主要驱动力,并结合与形式、性能及制造技术相关的限制条件进行评估。然而,当前的方法大多涉及对现有材料的研究。关于运算化材料设计的研究,即通过设计微观结构来开发新材料以应对性能问题,通常是在材料尺度上开展的,尚未应用于建筑设计过程。为解决这一问题,本文开发了一种名为 “基于性能的运算化设计中跨尺度材料微观结构组织”(I2MO_PCD)的方法,并分三个阶段进行阐述,包括:(1)识别不同类型的材料微观结构;(2)运算化材料设计;(3)原型制作。该方法运用了基于数据的材料建模与可视化,以及算法建模技术,随后进行各种性能模拟,并将其作为迭代过程的一部分。通过运算化设计出新的微观结构组织,这些组织主要分为线性 - 曲线型、晶体型和元球 - 沃罗诺伊型三大类。对不同性能分析的结果进行了比较,包括结构、辐射、日照时长、声学和热桥等方面。因此,通过设计和制造合成材料,确定了微观结构的几何组织、尺度以及材料类型在不同性能运算中的作用。
04
关 键 词
Keywords
Material microstructure / 材料微观结构
Computational design / 运算化设计
Performance computation / 性能运算
Architectural design / 建筑设计
05
章 节 标 题
Sections Title
1. Introduction / 引言
2. Methodology: Interscalable material microstructure organization in performance-based computational design / 研究方法:基于性能的运算化设计中跨尺度材料的微观结构组织
2.1. Identification of different types of material microstructures / 不同类型材料微观结构的识别
2.2. Computational material design / 运算化材料设计
2.2.1. Data-based microstructure modelling and visualization / 基于数据的微观结构建模与可视化
2.2.2. Computational geometry generation / 计算化几何生成
2.2.3. Performance simulations / 性能模拟
2.3. Prototyping / 原型设计
3. Results and discussion / 研究成果及讨论
3.1. Identification of different types in material microstructures / 对材料中不同类型微观结构的识别
3.2. Computational material design / 运算化材料设计
3.2.1. Data-based microstructure modelling and visualization / 基于数据的微观结构建模与可视化
3.2.2. Computational geometry generation / 计算化几何生成
3.2.3. Performance simulations / 性能模拟
3.3. Prototyping / 原型设计
3.4. Synthetic material design / 合成材料设计
3.4.1. Porosity percentage / 孔隙率
3.4.2. Anisotropy / 各向异性
4. Conclusion / 结论
06
主 要 插 图
Illustrations
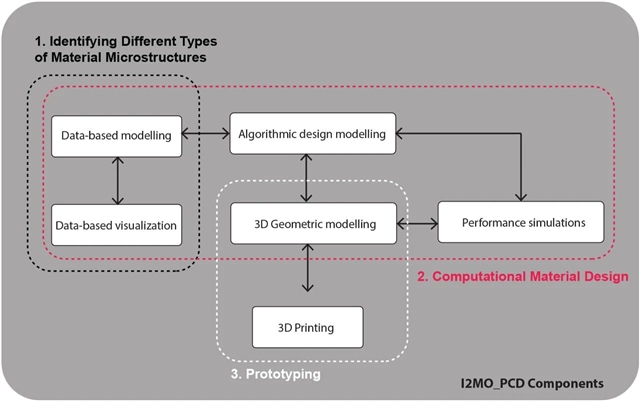
▲ 图一:I2MO_PCD各组件之间的关系。
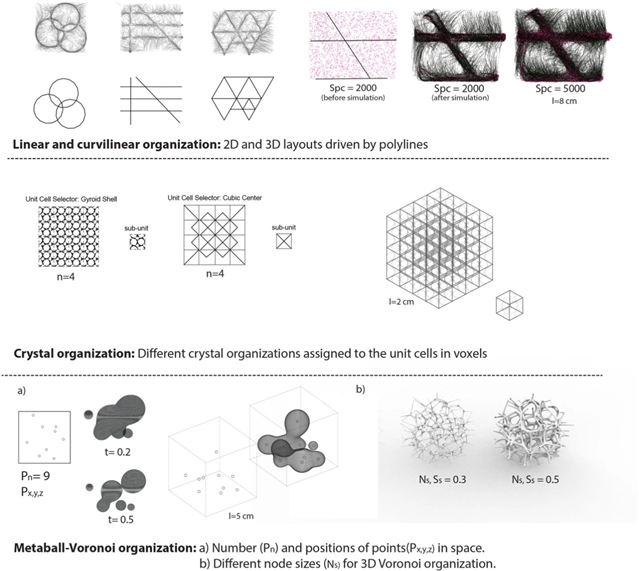
▲ 图二:Parameters related to the formation of the linear-curvilinear, crystal, and metalball-Voronoi organizations.
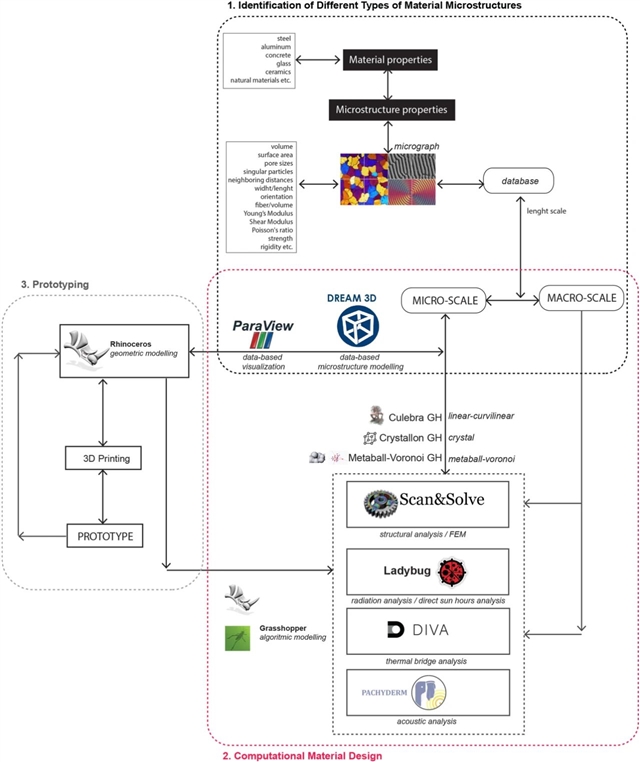
▲ 图三:I2MO_PCD方法,展现了该过程中所使用的数据流和数字工具。
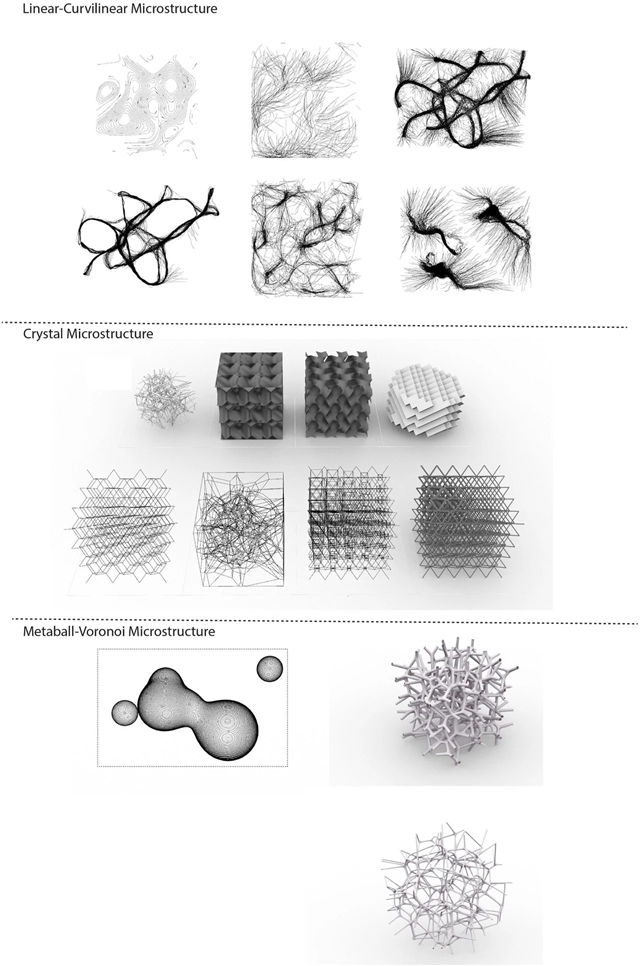
▲ 图四:Variations in algorithmically defined synthetic microstructure organizations.
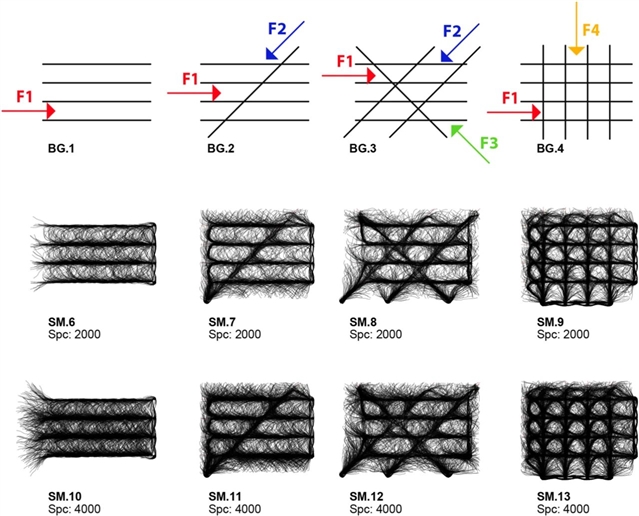
▲ 图五:Synthetic material design by altering the “BG” and “F” and to demonstrate anisotropy in linear-curvilinear organization.
07
作 者 介 绍
Authors’ Information

Sevil Yazici
Associate Professor
Department of Architecture
Istanbul Technical University, Turkey
《前沿》系列英文学术期刊
由教育部主管、高等教育出版社主办的《前沿》(Frontiers)系列英文学术期刊,于2006年正式创刊,以网络版和印刷版向全球发行。系列期刊包括基础科学、生命科学、工程技术和人文社会科学四个主题,是我国覆盖学科最广泛的英文学术期刊群,其中12种被SCI收录,其他也被A&HCI、Ei、MEDLINE或相应学科国际权威检索系统收录,具有一定的国际学术影响力。系列期刊采用在线优先出版方式,保证文章以最快速度发表。
特别声明:本文转载来源“科学网”,仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的来源,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载等相关事宜,请与我们接洽。